In times of serious laboratory staff shortages and dwindling medical laboratory scientist (MLS) graduates, having an effective laboratory workflow is crucial to maintain a productive lab. Today’s top public health labs (PHLs) are focused on how to develop and maintain efficient workflows so they can fulfill their mission to improve public health.
Efficient lab workflows share some common aspects, such as making the best use of resources — especially staffing — and automating redundant laboratory tasks to free MLSs for tasks that require their expertise. Having an ultraefficient lab workflow can improve morale, which aids in staff retention, and can improve your lab’s contribution to the nation’s PHL system.
What is Laboratory Workflow?
Laboratory workflow involves following predetermined processes and procedures to manage all aspects of laboratory testing from pre-analytical, through analytical, and post-analytical testing phases. See Figure 1. Workflow encompasses test ordering, instrument maintenance, restocking supplies, quality control procedures, reporting test results, and more. A lab workflow management process defines the specific tasks and people involved in producing an outcome, while a procedure is a detailed set of instructions for completing a specific task.
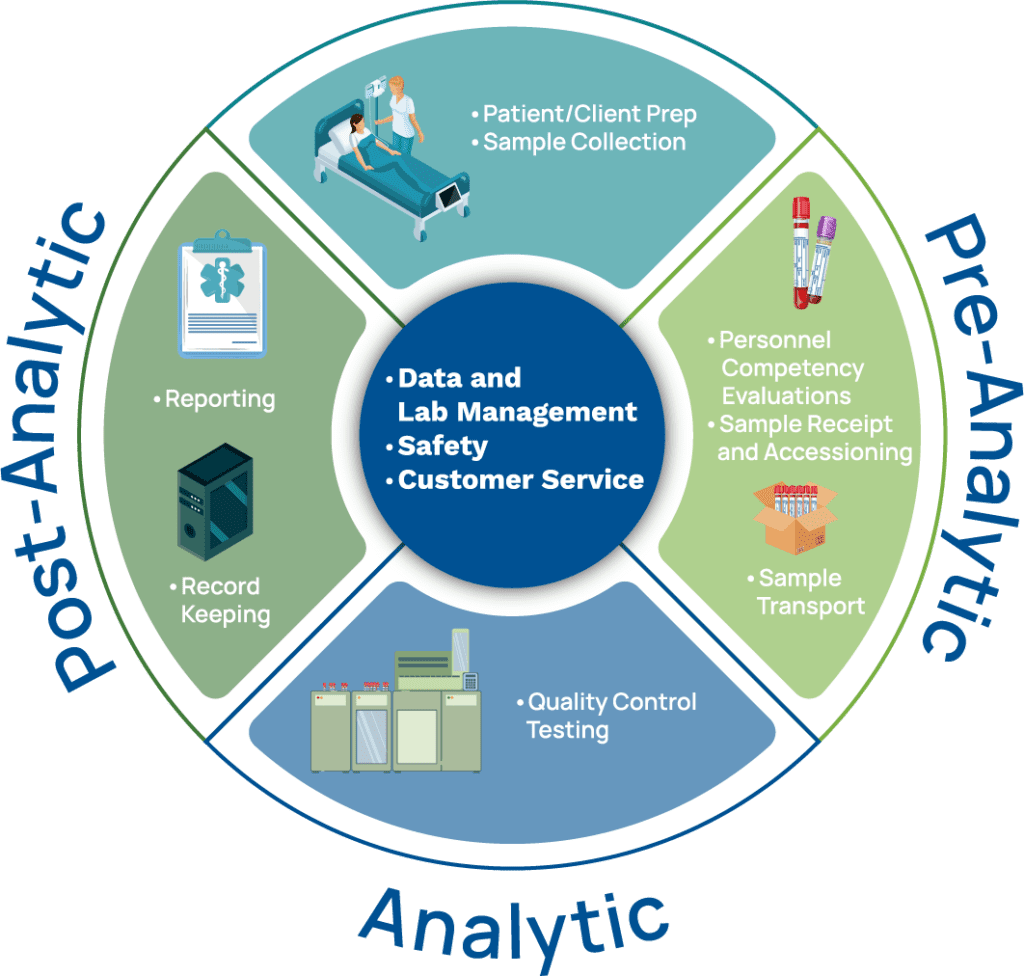
Specific to a public health laboratory, a workflow involves:
- Processing clinical and environmental lab tests
- Scheduling lab tests (including the ability to adapt to surges)
- Collecting samples for prescheduled tests
- Sample tracking/Chain of custody
- Manufacturing media, reagent, stains, controls, etc.
- Inventory control (including kits and forms)
- Laboratory reporting
- Statistical analysis and surveillance
- Laboratory billing
- Contract and grant management
- Managing personnel resources (training, education, etc.)
- Maintaining lab certifications/licensing
- Managing customer concerns
- Quality control and assessment
- Laboratory safety
- Laboratory mutual assistance2
For more information on PHLs, see our blog post What is the Public Health 3.0 Framework? Everything You Need to Know.
Characteristics & Benefits of an Effective Workflow
Alongside supporting specific processes and procedures, effective laboratory workflow management includes parameters that promote regulatory compliance and adherence to quality standards while simultaneously maximizing use of resources.
To facilitate the PHL’s main goals—to stop the spread of infectious diseases, improve public and environmental health, and mitigate other hazardous situations—the electronic sharing of data is necessary to speed communication during a public health crisis. Having a lab workflow that includes IT systems (electronic medical records, laboratory information systems, etc.) sharing data as part of an overall interoperable healthcare organization aids in informed decision making, provides greater access to real-time data, and improves the overall efficiency of patient care and public healthcare.
Promotes Regulatory Compliance & Adherence to Quality Standards
Every PHL requires various certifications depending on the specific type of testing performed. Regardless of the specific regulatory body, steps that help automate and ensure regulatory compliance should be woven into an effective laboratory workflow and, where possible, automated by the laboratory information system (LIS) or laboratory information management system (LIMS). The Public Health Informatics Institute, the Association of Public Health Laboratories (APHL), and numerous state and local PHLs have collaborated for years to promote LIMS adoption and efficient use.
A LIMS provides laboratories with the tools to effectively manage laboratory data and provide timely reports for surveillance and program management. This functionality improves the total testing process and allows for tracking of quality control and quality assessment (QA) initiatives.2 Functionality (rules, data mining, etc.) and data collection and tracking within the LIMS can automate workflow steps to reduce errors and speed up lab processes. Data within the LIMS is readily available for inspections and to track key performance indicators and QA measures.
Maximizes Laboratory Resources
Effective lab workflow management can also help PHLs maximize laboratory resources. By using available technology to automate steps and standardize lab processes where feasible, laboratory scientists’ time can be better spent on tasks that use their specialized training. With an industry facing continued staffing shortages, it is imperative that laboratory professionals’ time is not wasted on menial, repetitive tasks that can be automated. Many PHLs use tools such as Lean Six Sigma to find and remove bottlenecks, remove intermediaries, remove unnecessary steps, and to standardize information and patient flow. Read Tulare County Public Health Lab’s Lean Journey for an example.
Promotes Interoperability
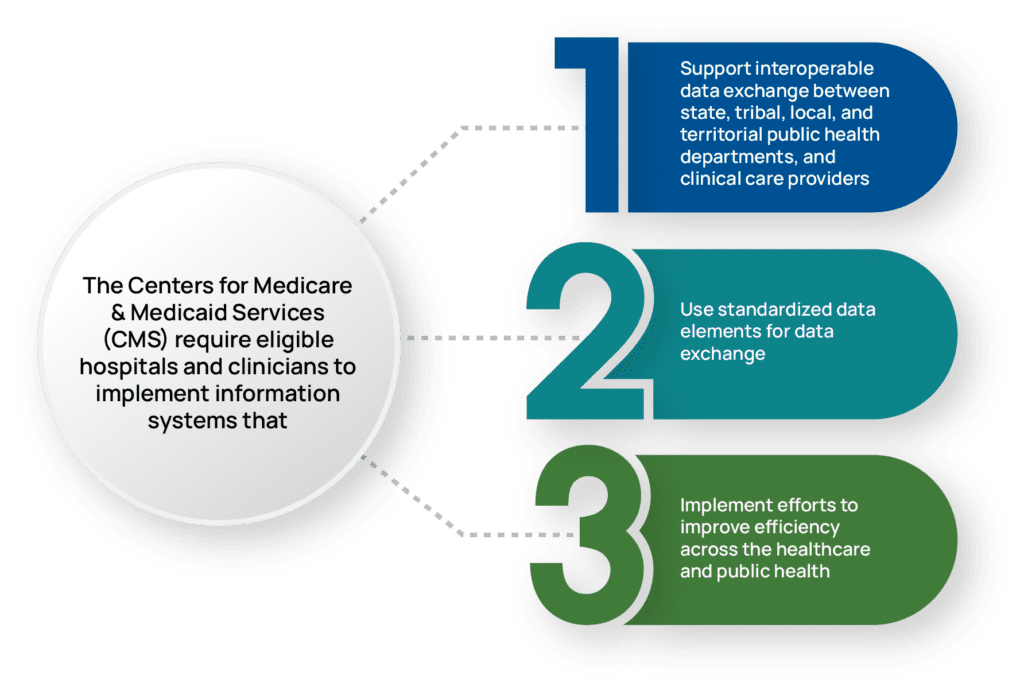
The PHL’s biggest asset is its data. Data within each laboratory and healthcare organization needs to be accessible to those who need it for patient care and public health stewardship. The overarching goal of data interoperability within our healthcare system is that, by improving electronic reporting, we see subsequent improvements in patient care; see Figure 2.
How Can Public Health Labs Improve Workflow?
The first step to improving lab workflow is to assess your current workflow for areas that can be improved. Then, prioritize the changes that need to be made. If the list is overwhelming, start with small, impactful changes. As always, it can be helpful to set SMART (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, time-bound) goals. Consider these questions:
- Where can you adapt your testing menu to standardize testing platforms?
- What processes in the lab can be automated by the LIMS?
- Are there result evaluation rules that can reduce errors (e.g., test routing, duplicate test orders, autoverification)?
- Can your lab automate report delivery through HL7 interfacing?
- Are there paper processes that can be replaced with the LIMS?
Start with Small, Yet Impactful Changes
A common mistake when developing laboratory workflows is approaching the endeavor from a macro level. This approach can be overwhelming and may lead to missing important steps or areas that can be improved. By identifying a few high-impact processes to focus on, you can get some quick wins right from the start. For example, if autoverifying results is one of your lab workflow efficiency goals, start with autoverifying one test, and expand from there. Likely, the process will become easier as you proceed through the testing menu.
Identify Key Obstacles & Constraints
Another planning step in working toward a more effective lab workflow is to identify and mitigate obstacles and constraints. Consider these questions:
- Will the change require administrative support?
- Will the change have staff support or resistance?
- What will the associated costs be?
- Are patients involved in the process improvement?
- Will you need to provide training?
Standardize Laboratory Services & Processes
Standardization of laboratory processes and procedures can improve both lab efficiency and quality. Variation in processes can have a significant negative impact on lab efficiency. Standardized policies, procedures, and methodologies help improve manageability, quality, and efficiency due to decreased redundancy and opportunity for errors. Removing disparities can improve efficiency, patient satisfaction, and quality of care.
When processes and methodologies are not standardized, the differences in testing methodologies can be confusing and potentially lead to misinterpreted results. Plus, standardization allows for uniformity of electronic health record (EHR) and LIS/LIMS setup across locations, reducing opportunities for misinterpretation.4 Standardization allows for effective timing and planning, which translates into efficiency improvements. Standard operating procedures help reduce variability in the output of the process, improving quality.
Integrate Data Standards
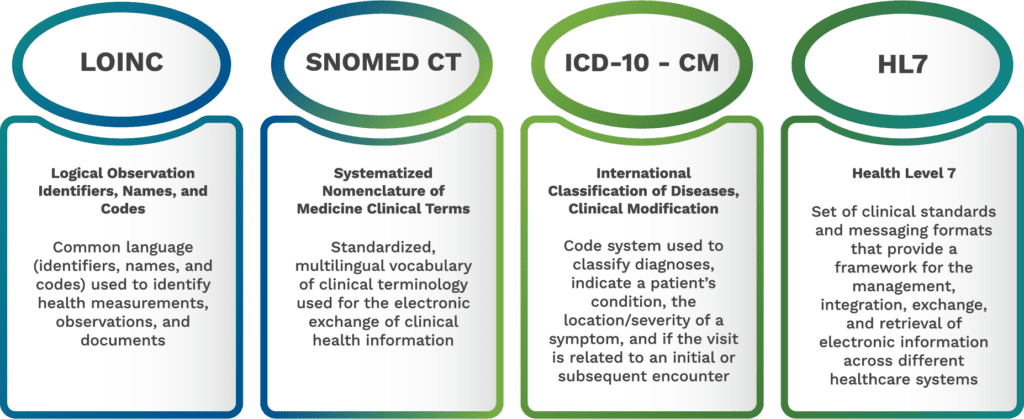
Integrated systems share data and communicate by using common data standards (LOINC, SMOMED, ICD-10, HL7). See Figure 3. Data integration streamlines laboratory reporting and facilitates data comparison and reconciliation, which supports interoperability.
Automate Lab Processes Where Possible
Automation opens another opportunity for test processing standardization. LIMS capabilities can automate many areas of the test ordering, routing, and reporting lab process. The LIMS also has sample and data tracking and can automate report creation for key stakeholders and inspectors.
- Are there redundant processes within your lab workflow that can be automated with technology?
- Would it benefit your lab to add an automated liquid handler or an electronic pipettor?
Implement Software that Addresses the Specific Needs of PHLs
The LIMS provides the infrastructure for PHLs to organize, process, and streamline many lab operations. Laboratories with an effective LIMS can manage higher specimen volumes and improve their overall business operations, making contributions to improvements in patient care and protecting the public health. PHLs using LIMS benefit from more reliable specimen tracking, accurate analysis, and data exchange that enables timely reporting. The PHL LIMS reduces errors, improves testing turnaround time, increases compliance with quality standards, and helps contribute to improved patient outcomes. See LIMS high-level requirements specific to PHLs.
How a LIMS Helps Public Health Labs Streamline Operations & Improve Workflow
PHLs require a LIMS, not only to support automation and standardization of lab workflow processes, but also to allow for the electronic exchange of data in a timely manner. PHLs sit in a hierarchy of laboratories that work together to address public health emergencies. Having an electronic communication system to exchange results between these laboratories and their partners is vital to our public health system.
Data Management to Support Public Health Surveillance
Public health and clinical laboratories support testing for patients, surveillance, and outbreak responses. This lab data is used to monitor diseases and outbreaks, distribute workload across laboratories, and to ensure quality. The data is vital for epidemiology teams and prevention programs. PHLs use a LIMS as a data repository to support testing and outbreak response.
Electronic Lab Reporting (ELR) Integration
Electronic laboratory reporting (ELR) for public health is the transmission of laboratory data from laboratories to state and local public health departments, healthcare systems, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and is an integral contribution to interoperability between healthcare systems. ELR integration helps PHLs improve workflow by automating and speeding up the delivery of lab testing for state reportable diseases. This automation of reporting contributes to increased efficiency and streamlined operations and enhances PHL surveillance and preparedness capacity.
Orchard offers ELR interfaces to link laboratories to public health entities and automate the transmission of laboratory data for reportable conditions. Orchard’s solutions are ONC-certified (Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology) and compliant with HL7 standards, allowing laboratories to electronically report results to the state’s surveillance system to monitor critical data in a timely manner.
Laboratory Response Network (LRN) Integration
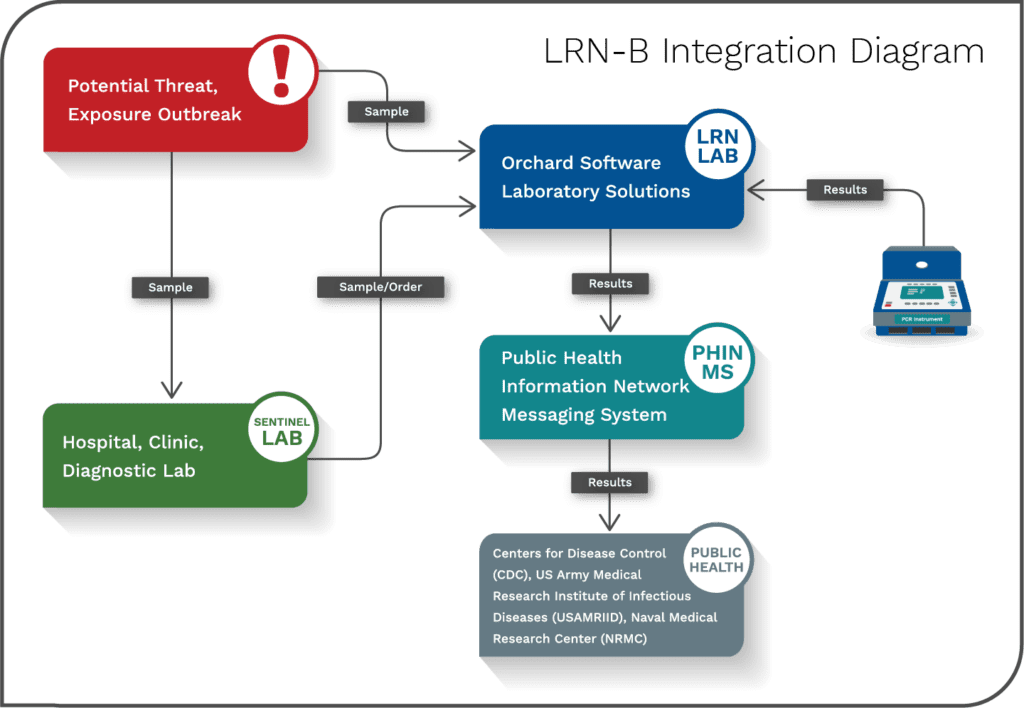
The CDC established the Laboratory Response Network (LRN) as a network of laboratories that respond to biological and chemical threats and other public health emergencies. The LRN includes state and local public health, veterinary, military, and international labs. The Public Health Information Network Messaging System (PHINMS) is CDC-provided software that enables labs to reliably exchange critical and sensitive data among disparate systems.
Orchard has developed an interface to the CDC’s PHINMS with a variety of possible deployment options. See Figure 4. This interface enables LRN labs to report their results to the CDC electronically to quickly recognize, rule out, or refer potential biothreat agents.
Support for Diverse Testing Menu
Most PHLs have a broad testing menu that includes clinical and environmental laboratory testing. Orchard’s systems provide the flexibility required by the diverse testing menu found in the PHL environment, enabling the laboratory to manage testing for suspected cases of infectious and environmental diseases. Orchard’s systems’ adaptability accommodates parameters needed for esoteric sample types, ranging from water or food to tick testing for rabies. Having a LIMS that supports both testing types improves PHL efficiency.
Decision-support Rules & Lab Analytics
An effective LIMS enables advanced decision-support rules and provides analytics that help streamline operations within a PHL. Advanced decision-support rules enable the systematic development of decision trees and algorithms for reflex testing, result routing, charge capture, and test interpretation. Data mining and analytics enable monitoring and documentation of compliance activities and reporting of inconsistent findings for corrective actions.
How Orchard Contributes to Lab Workflow Improvements
In an unprecedented time, faced with a pandemic, severe staffing shortages, government regulations that affect reimbursements, and continued change, top laboratories find ways to bring efficiencies into their workflow that allow them to continue to provide a level of excellence and a focus on taking care of patients.
Orchard Software’s web-based solutions can address the advanced IT needs of a diverse testing menu and eliminate many of the concerns PHLs face regarding electronic lab reporting. Offering complete laboratory system integration, decision-support rule capabilities, configurable analytics, and case management tools, Orchard’s systems allow PHLs to efficiently track clinical and environmental laboratory test data, respond to public health emergencies, and capture key performance analytics. For more information, visit Orchard’s PHL page or contact us at (800)-856-1948 or sales@orchardsoft.com.

